High-Altitude Disease (Brisket Disease) in Ruminants, Primates, Rodents and Wallabies at a Mexican Zoo
Abstract
This study documents for the first time 18 cases (Table 1) of right-sided hypertrophic cardiomyopathy associated with pulmonary arteriosclerosis in zoo animals, including 10 maras (Dolichotis patagonum), one nilgai antelope (Boselaphus tragocamelus), one scimitar-horned oryx (Oryx dammah), two cotton-top tamarins (Saguinus oedipus oedipus), two capybaras (Hydrochaeris hydrochaeris) and two wallabies (Macropus rufogriseus) housed at Africam Safari (Puebla, Mexico). In two ruminants (cases 1 and 2), death was attributed to right-sided congestive heart failure. In the rest of the cases, cardiomyopathy was considered incidental and not related to the cause of death.
Table 1. Clinical history of 18 cases of antelopes, rodents, primates and wallabies with
right-sided cardiac hypertrophy and pulmonary arteriosclerosis at Africam Safari Zoo in México
|
Case no.
|
Species
|
Sexa
|
Ageb
|
Weight (kg)
|
Cause of death
|
|
1
|
Oryx dammah
|
M
|
1 y
|
NRc
|
Congestive heart failure
|
|
2
|
Boselaphus tragocamelus
|
F
|
1.5 y
|
NR
|
Congestive heart failure
|
|
3
|
Dolichotis patagonum
|
M
|
Young adult
|
6.7
|
Possible acute heart failure
|
|
4
|
Dolichotis patagonum
|
F
|
Young adult
|
6.8
|
Euthanasia—bacterial pododermatitis
|
|
5
|
Dolichotis patagonum
|
M
|
Adult
|
7.2
|
Hyperthermia
|
|
6
|
Dolichotis patagonum
|
F
|
2 y 8 m
|
7.8
|
Trauma
|
|
7
|
Dolichotis patagonum
|
M
|
Adult
|
7.2
|
Trauma
|
|
8
|
Dolichotis patagonum
|
M
|
Juvenile
|
6.4
|
Trauma
|
|
9
|
Dolichotis patagonum
|
M
|
2 y 8 m
|
7.2
|
Trauma
|
|
10
|
Dolichotis patagonum
|
F
|
Adult
|
8
|
Trauma
|
|
11
|
Dolichotis patagonum
|
F
|
Young adult
|
6.8
|
Trauma
|
|
12
|
Dolichotis patagonum
|
M
|
Juvenile
|
6.4
|
Possible acute heart failure
|
|
13
|
Saguinus oedipus oedipus
|
F
|
4 m
|
0.114
|
Bacterial infection
|
|
14
|
Saguinus oedipus oedipus
|
M
|
Adult
|
0.335
|
Bacterial infection—wasting marmoset syndrome
|
|
15
|
Hydrochaeris hydrochaeris
|
M
|
Adult
|
NR
|
Trauma
|
|
16
|
Hydrochaeris hydrochaeris
|
M
|
Adult
|
NR
|
Trauma
|
|
17
|
Macropus rufogriseus
|
F
|
Adult
|
12
|
Gastric perforation
|
|
18
|
Macropus rufogriseus
|
F
|
Adult
|
9.2
|
Bacterial infection
|
aM=male; F=female
by=year; m=month
cNR=not recorded
Grossly, all cases had cardiomegaly, with right-sided concentric hypertrophy (Table 2), often with dilatation of the right ventricle. The right to left ventricular thickness ratio ranged 1:1 to 1:1.6 in 15 cases. Sixty-one percent had arteriosclerosis of the pulmonary trunk. Histologically, all cases had medial hypertrophy of the small- and/or medium-sized pulmonary arteries. Other pulmonary arterial lesions found in fewer cases are also listed in Table 2. Chronic passive congestion of the liver was observed in two cases.
Table 2. Pathologic findings in 18 cases of antelopes, rodents, primates and wallabies with right-sided cardiac hypertrophy and pulmonary arteriosclerosis at Africam Safari Zoo in México.a
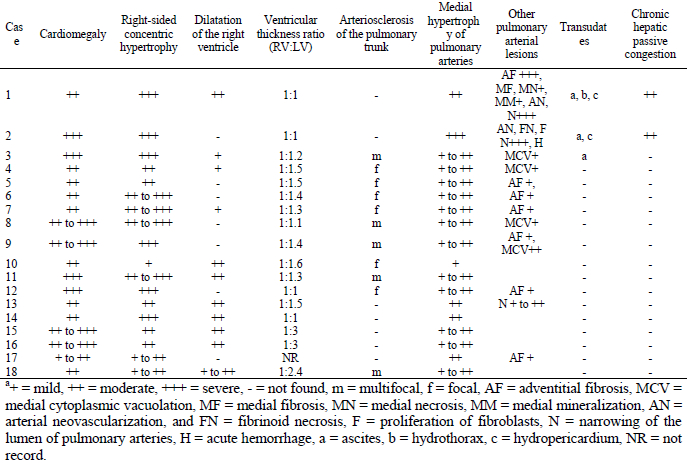
The high prevalence of right-sided cardiomyopathy at Africam Safari in the study period (2000–2005) is unusual. Based on the presence of pulmonary arteriosclerosis,3 the absence of stenosis of the pulmonary valve and severe pulmonary diseases,2 and the fact that this zoo is located at 2,126 m above sea level, right-sided hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in these cases was attributed to hypoxia of high altitude.1-3 Cardiomyopathy was considered subclinical in most cases but caused fatal congestive heart failure in two juvenile ruminants.
Literature Cited
1. Ge, R.L., and G. Helun. 2001. Current concept of chronic mountain sickness: pulmonary hypertension-related high-altitude heart disease. Wilderness Environ Med. Fall 12(3):190–194.
2. Van Vleet, J.F., and V.J. Ferrans. 2001. Cardiovascular system. In: Thomson’s Special Veterinary Pathology. 3rd ed. Pp. 197–233.
3. Stenmark, K.R., J. Fasules, D.M. Hyde, N.F. Voelkel, J. Henson, A. Tucker, H. Wilson, and J.T. Reeves. 1987. Severe pulmonary hypertension and arterial adventitial changes in newborn calves at 4,300 m. J Appl Physiol. 62(2):821–830.