Abstract
Giant anteaters (Myrmecophaga tridactyla) are highly specialized insectivores with low energy requirements compared with similar-sized mammals and an exceptional feeding apparatus and behavior.6,7 Common health problems which have been attributed to suboptimal nutrition are loose stool or diarrhea, anorexia, tongue tip constriction or vitamin K deficiency.4,8 Traditional, natural in-house diets typically include dog kibble, cereals, honey, milk products, meat and insects.5 Simpler (and more rational) diets consisting of a mixture of commercial dry feeds for cats and leaf eaters have been promoted particularly in the U.S.2 In recent years commercial complete diets have become available. Potential advantages of such diets are nutritional adequacy, standardized quality, less preparation time and facilitated exchange of animals between institutions. However, it has been reported that anteaters may be very reluctant for a diet change and may react with prolonged refusal.1,3 For veterinarians and curators it is difficult to decide what period of anorexia and what percent of weight loss is acceptable. Here we report observations from three consecutive dietary changes (Diet A, B, C; Table 1) made with three giant anteaters (Figure 1).
Table 1. Composition of commercial diets for insectivorous mammals.
|
Company
|
Diet A
“Mazuri Insectivore Diet
|
Diet B
“Mazuri Termant”
|
Diet C
“Insectivore”
|
|
|
5MK8”Purina Mills, St. Louis, MO 63166 USA
|
PO BOX 705 Witham, Essex CM8 3TH, UK
|
Kliba Nafag, Provimi Kliba AG, 4303 Kaiseraugst, Switzerland
|
|
Crude fat
|
12.0 %
|
10.2 %
|
10.0 %
|
|
Crude protein
|
28.5 %
|
28.3 %
|
29.7 %
|
|
Crude fiber
|
9.6 %
|
10.9 %
|
13.0 %
|
|
Ash
|
6.5 %
|
6.1 %
|
7.4 %
|
The animals were clinically healthy and stool consistency was firm. The changes took place over a period of 3 yr. Prior to the diet change, giant anteaters at Zurich Zoo were fed with a mixed natural in-house diet of minced meat, dog pellets, low fat curd cheese, cereals, shrimp meal, honey, seasonal fruits, boiled eggs, chitin powder, mineral/vitamin supplement and sifted peat.8 Diet A was completely refused by all three animals and the trial was stopped after three weeks of reduced and intermittent intake resulting in increased aggression against keepers and tapirs (which share the exhibit with anteaters). The loss of weight of 6% was considered not acceptable for two lactating females. After 14 mo on the previous traditional diet, a second attempt with diet B was made. This diet was accepted with increasing amounts over a period of 4 mo but a weight loss of 6–24% occurred after 18 mo on this diet, and all animals showed repeatedly loose stool. Due to high cost of diet B and irregular supply, a third change to diet C became necessary. Both female anteaters immediately started to eat diet C well and to increase weight. With diet C all animals showed loose stool, which was eliminated by adding peat to the diet (115 gr to 260 gr of diet C, per animal, twice a day), which represented an increase of the content of crude fiber from 13% to 17% in dry matter. Within 12 mo the two females increased their body weight by up to 33% (Figure 1).The male showed intermittent reluctance to eat the diet and eventually died of causes considered unrelated to the diet change.
Figure 1. Changes in body mass of three adult giant anteaters (Myrmecophaga tridactyla) during three diet changes from a mixed natural in-house diet to a commercial complete diet
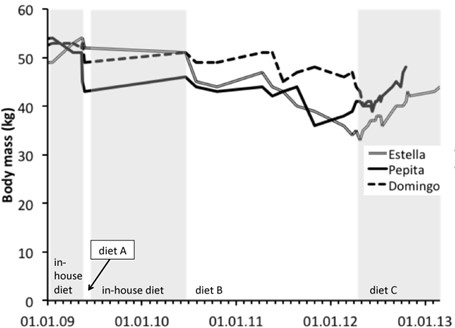
A possible reason for the complete refusal of diet A may have been the fact that it was provided as granules first, which the animals did not seem to like, and only as ground powder later. Diets B and C were powdered from the beginning. It should be noted that diet A appears to be well accepted by anteaters at other institutions.8 Therefore, we think that the history presented here does not represent a test case of the three diets, but illustrates the problem in overcoming individual feeding preference inertia in this species. The transition from the traditional custom made to a commercial diet resulted in a timesaving effect of approximately 45 min per day.
In conclusion, we observed that the introduction of commercial complete diets may result in important weight loss of up to 20%. In lactating females, a weight loss of more than 6% was considered not acceptable. Occurrence of loose stool appears to be a problem observed with introduction of commercial complete diets in giant anteaters in general and needs to be addressed with addition of fiber into the diet.
Literature Cited
1. Clauss, M., M. Stahl, C. Osmann, S. Ortmann, and J.M. Hatt. 2010. Feeding and body mass development in giant anteaters (Myrmecophaga tridactyla). Proc. 6th Eur. Zoo. Nutr. Conf. 42.
2. Edwards, M.S., and A. Lewandowski. 1996. Preliminary observations of a new diet for Giant anteaters (Myrmecophaga tetradactyla). Proc. Am. Assoc. Zoo Vet. Annu. Conf. 496-499.
3. Gull, J., T. Rothlin, M. Clauss, and J.M. Hatt. 2012. Never give up: changing giant anteaters (Myrmecophaga tridactyla) to a new, complete diet at Zurich Zoo. Proc. 7th Eur. Zoo. Nutr. Conf. 4.
4. Morford, S., and M.A. Meyers. 2003. Giant Anteater (Myrmecophaga tridactyla) Health Care Survey. Edentata. 5: 5–20.
5. Morford, S., and M.A. Meyers. 2003. Giant anteater (Myrmecophaga tridactyla) diet survey. Edentata. 5: 20–24.
6. Reiss, K.Z. 2000. Feeding in myrmecophagous mammals. In: Schwenk, K., (ed.). Feeding-Form, Function, and Evolution in Tetrapod Vertebrates, Academic Press, San Diego USA. 459-485
7. Stahl, M., C. Osmann, S. Ortmann, M. Kreuzer, J.M. Hatt, and M. Clauss. 2012. Energy intake for maintenance in a mammal with a low basal metabolism, the giant anteater (Myrmecophaga tridactyla). J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 96:818-824.
8. Steinmetz, H.W., M. Clauss, K. Feige, T. Thio, E. Isenbügel, and J.M. Hatt. 2007. Recurrent tongue tip constriction in a captive Giant Anteater (Myrmecophaga tridactyla). J. Zoo. Wildl. Med. 38: 146–149.